1 基本介绍
hyperopt通过在超参空间内快速搜索,寻找最优的模型超参
- 目前已实现搜索算法:随机搜索、TPE和自适应TPE
- 低代码,易上手;支持分布式运算
注意:虽然该项目有6.6k个⭐,但已经有一年半未更新
截至撰写本文的230315,此项目的上次更新日期是211129
补充说明:对tpe算法原理感兴趣的读者可参阅论文阅读-TPE算法
2 简单上手
- 最简单的官方示例:
# 定义目标函数
def objective(args): # objective = c1+c2^2
case, val = args
if case == 'case 1':
return val
else:
return val ** 2
# 定义搜索空间
from hyperopt import hp
space = hp.choice('a',
[
('case 1', 1 + hp.lognormal('c1', 0, 1)), # 定义参数c1的取值范围在0~1
('case 2', hp.uniform('c2', -10, 10)) # 定义参数c1的取值范围在-10~10
])
# 在给定空间下搜索目前最优的参数取值
from hyperopt import fmin, tpe
best = fmin(objective, space, algo=tpe.suggest, max_evals=100) #
print(best)
# -> {'a': 1, 'c2': 0.01420615366247227}
print(hyperopt.space_eval(space, best))
# -> ('case 2', 0.01420615366247227}
fmin函数的参数说明:
algo参数指定搜索算法,目前只支持tpe.suggest和random.suggestmax_evals参数表示目标函数的最大评估次数
- 基于TPE(Tree-structured Parzen Estimator Approach)的优化SVM的代码示例:
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from hyperopt import hp, fmin, tpe, space_eval
import pandas as pd
# 导入数据
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# step1: 定义目标函数
def objective(params):
# 初始化模型并交叉验证
svc = svm.SVC(**params)
cv_scores = cross_val_score(svc, iris.data, iris.target, cv=5)
# 返回loss = 1 - accuracy (loss必须被最小化)
loss = 1 - cv_scores.mean()
return loss
# step2: 定义超参搜索空间
space = {'kernel':hp.choice('kernel', ['linear', 'rbf']),
'C':hp.uniform('C', 1, 10)}
# step3: 在给定超参搜索空间下,最小化目标函数
best = fmin(objective, space, algo=tpe.suggest, max_evals=100)
返回: best_loss: 0.013333333333333308(即accuracy为0.9866666666666667)
# step4: 打印结果
print(best)
返回:{'C': 6.136181888987526, 'kernel': 1}(PS:kernel为0-based index,这里1指rbf)
3 进阶使用
- hyperopt支持对objective进行更丰富的定义以保留搜索的过程信息:
import pickle
import time
from hyperopt import fmin, tpe, hp, STATUS_OK, Trials
def objective(x):
return {
'loss': x ** 2,
'status': STATUS_OK,
# -- store other results like this
'eval_time': time.time(),
'other_stuff': {'type': None, 'value': [0, 1, 2]},
# -- attachments are handled differently
'attachments':
{'time_module': pickle.dumps(time.time)}
}
trials = Trials() # 用于信息的存储
best = fmin(objective,
space=hp.uniform('x', -10, 10),
algo=tpe.suggest,
max_evals=100,
trials=trials)
print(best)
- 针对不同类型的数据可制定不同的搜索空间
- 针对分类参数,使用
hp.choice;针对整数参数,使用hp.randint - 针对浮点参数,使用
hp.uniform;针对服从正态分布的随机参数,使用hp.normal - 针对服从对数正态分布的随机参数,使用
hp.lognormal;
from hyperopt import hp
space = hp.choice('classifier_type', [ # 根据分类器类型区分不同的搜素空间
{
'type': 'naive_bayes', # 贝叶斯分类器
},
{
'type': 'svm', # 支持向量机分类器
'C': hp.lognormal('svm_C', 0, 1),
'kernel': hp.choice('svm_kernel', [ # 不同核方法及其对应的参数搜索空间
{'ktype': 'linear'},
{'ktype': 'RBF', 'width': hp.lognormal('svm_rbf_width', 0, 1)},
]),
},
{
'type': 'dtree', # 决策树分类器
'criterion': hp.choice('dtree_criterion', ['gini', 'entropy']),
'max_depth': hp.choice('dtree_max_depth',
[None, hp.qlognormal('dtree_max_depth_int', 3, 1, 1)]),
'min_samples_split': hp.qlognormal('dtree_min_samples_split', 2, 1, 1),
},
])
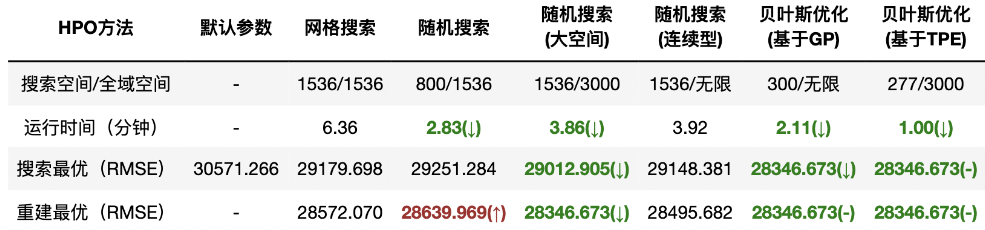 图源:
图源:
20230315到此一游